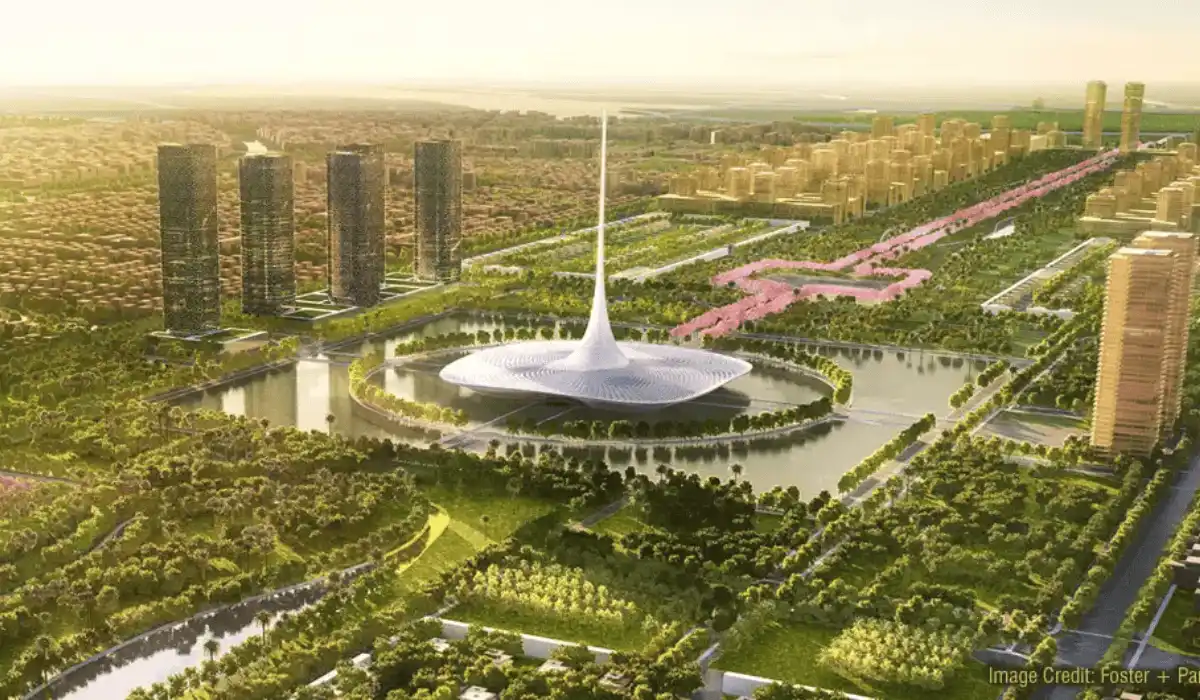
Largely recognised as the “Smart City of the Future”, the Gujarat International Finance Tech (GIFT) City has evolved as a flagship project in the FinTech domain. Promoted as India’s first greenfield smart city project, the GIFT city was conceived as the growth capital of India. The idea for GIFT was birthed in 2007 during the Vibrant Gujarat Global Investor Summit. The Summit was conceptualised in 2003 by the Prime Minister of India, Shri. Narendra Modi (then Chief Minister of Gujarat) for establishing Gujarat as a preferable state for investment in India. Hence, GIFT City was planned as a new financial and technological gateway to India for the world.
The purpose of GIFT City was to bring India on par with global Central Business Districts (CBDs) such as the ones in Singapore, Dubai, La Defense Paris, Hongkong, and London Dockyards. This first-of-its-kind city in India is intended to significantly boost the economy of Gujarat and establish India as a Centre of Excellence in the Information Technology (IT) and Finance sector worldwide. The mass creation of employment and improving the liveability index of people were the underlying reasons for attracting investment in the state through the GIFT City project.

Project Timeline
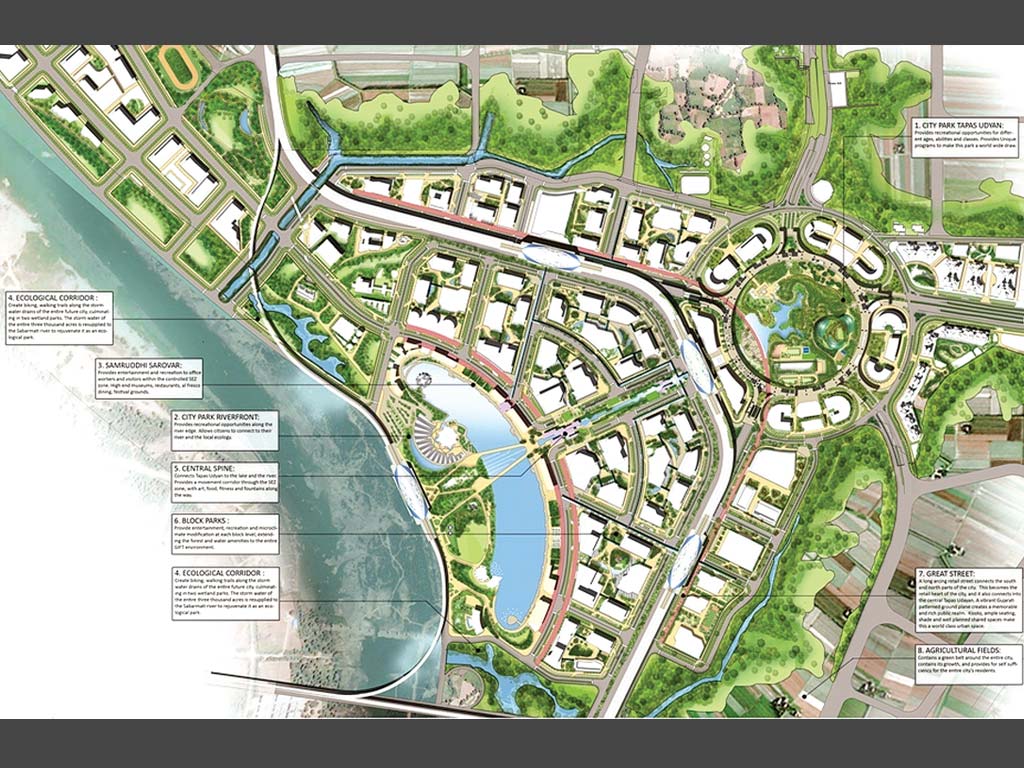
Although conceptualised in 2007, the groundwork for GIFT City began in 2012 when the foundation stone was laid for the project. The city was originally developed as a joint venture between the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City Company Limited (GIFTCL). and the Infrastructure Leasing and Financial Services Ltd (IL&FS). A greenfield land along the banks of river Sabarmati in Gandhinagar was selected as the site for GIFT City. The site has an area of 8.9 square kilometres (886 hectares) with a proposed built-up area of 5.76 square kilometres (576 hectares).
In 2011, GIFT City officials began to invite international companies who wished to expand their business across the globe. The city considered investments from private equity companies, banks, asset management companies, and insurance companies. The project was supposed to be developed in 3 phases of 4 years each. In 2012, the GIFT Urban Development Authority (GIFT UDA) was established to chalk out the development plan of the city with town planning schemes and construction layouts. The project demands investment of Rs.10,000 crores from domestic and international markets.
Design Approach and Stakeholders
Planned as an integrated sustainable development the GIFT City is zoned into three key parts -a Multi-Service Special Economic Zone (SEZ), an International Finance Service Centre (IFSC), and a domestic Financial Centre. Within these zones, the land was proposed to be developed for commercial, residential, institutes, retail, and recreational purposes. The planning schemes are finalised with the intent of promoting seamless international and domestic financial services.

The urban design and architecture of the city have been undertaken by the East China Architectural Design and Research Institute (ECADI) and Fairwood Consultant India. They have devised a master plan with state-of-the-art infrastructure encompassing all elements of the modern urban fabric. British Telecom has provisioned the Information, Communication, and Technology Advisory Services in the GIFT City. The project has undergone environmental assessment through IL&FS Ecosmart ltd. Power management of the project has been done by ABB Group.
Planning and Infrastructure of GIFT City
GIFT City is strategically located at the heart of Gujarat for easy accessibility for all. The city is well connected in all directions with 4-6 state and national highways. GIFT City is located in close proximity to the Ahmedabad International Airport with a distance of 12km. More so, a double corridor metro rail system is planned to connect the airport and other parts of Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar with the GIFT City for facilitating a Mass Rapid Transport System.

The planning of GIFT City has been done with the idea of improving the quality of life of people in the country. The city is designed to fulfil the needs of people for a safe and clean environment by offering world-class amenities and services. Considering the scale of the project, the designers have worked towards reducing its urban impact. The project is designed to have low energy consumption, reduced waste, and protect the diverse natural species in and around the site. The modularity of building infrastructure and services planned for the city make them appropriate for scalability in the distant future.
The GIFT City is also labelled as an Eco-City because it represents a vibrant hub of western India supporting business-oriented yet environment-sensitive developments. The city’s development emulates idealistic principles of life and liveability through its growth. Such futuristic ideas and world-class infrastructure has brought GIFT City into the global limelight. The project has won accolades from reputed global forums for its successful implementation of District Cooling Systems, Automated Waste Collection Systems, and underground utility tunnels.
The first phase of the GIFT City spanned from 2012 to 2016 under which more than 1.4 square kilometres of land has been developed for commercial, residential purposes. From 2016 to2020, the project entered the second phase of construction facilitating offshore and international financial services.
The Current State of Affairs

The GIFT City project is expected to be completed in its third phase spanning from 2020 to 2024. Companies such as Tata Consultancy Services, Lemino Agro INDIA Pvt Ltd., and Dholera Metro City has fully operational commercial offices based in GIFT City. However, a news article published by The Indian Express suggests that only 18-20 percent of the proposed work for GIFT City has attained completion. The land which should have been developed for 2/3rd of its portion still appears considerably vacant. A publication quotes the current status of the project as a “patchwork of state-of-the-art” facilities.
While the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has been a significant contributor to slowing down the project, other economic concerns have also been looming. The incapacity of the Indian Rupee to be freely convertible has posed restrictions on certain overseas transactions which has reduced the magnetism of the GIFT City project for global corporate companies. With such speculations around the development of India’s one-of-its-kind FinTech project, it would be interesting to see when the project achieves its glorified vision or if it remains a plan on paper.
Sources:
- Planned as the next Singapore in 2012, Gujarat’s Gift city still remains a work in progress
- Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT)
- Explained: What is the status of Gujarat’s GIFT city project?
- GUJARAT INTERNATIONAL FINANCE TEC-CITY (GIFT) PROJECT
Disclaimer: The information contained herein have been compiled or arrived at, based upon information obtained in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. The opinions expressed within the content are solely the author’s and can be subject to change. The image featured in this article is only for illustration purposes. If you wish the article to be removed or edited, please send an email to editor@biltrax.com
Discover more from Biltrax Media, A Biltrax Group venture
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.